Thank you to everyone who signed up to our plant swap scheme!
All vouchers have now been claimed!
Follow the resources on this page for useful tips removing your garden cotoneaster
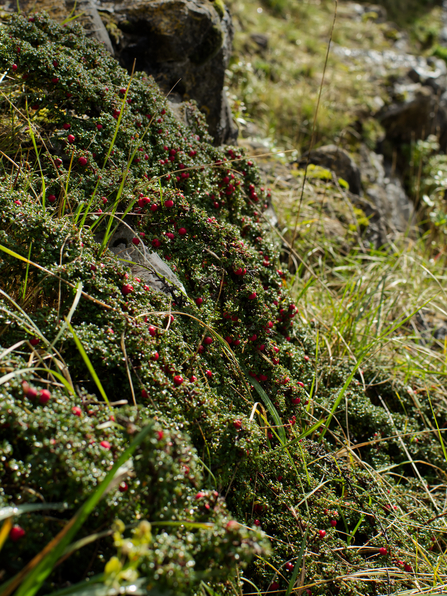

Cotoneaster smothering limestone grassland ©Craig Wade
What is the Plant Swap Scheme?
As part of the Limestone Grassland Restoration Project, the scheme aims to reduce the spread of invasive non-native cotoneaster onto our extraordinary limestone grasslands.
These grasslands are some of the most plant and insect-rich habitats in the UK and can have over 40 plant species per square metre. Unfortunately, our limestone grasslands are at risk and now being smothered by cotoneaster- having a devastating effect on wildlife.
Cotoneaster berries are easily dispersed by birds causing the invasive to progressively spread. Acting as a seed source, garden cotoneaster is escalating this issue.
How can you help?
Most of our gardens contain plants that are not native to the UK - they originally came from another part of the world. While non-native plants can help us create beautiful ornamental displays to enjoy, if they escape into the wild some can become invasive.
- Reduce the spread of cotoneaster into the wild, by replacing your garden cotoneaster with a wildlife friendly alternative ⇒ Gardening without harmful invasive plants.
- Please only remove cotoneaster from your own garden! Report cotoneaster sightings on public land using the free INNS Mapper app
Find our helpful tips of how to responsibly dispose of your unwanted cotoneaster below:
1. Place sheeting around the base of your unwanted cotoneaster - this will help catch any berries that may fall
2. Uproot or cut the cotoneaster using lopper or secateurs
3. Treat the exposed stumps with an appropriate herbicide
4. Take all material to a disposal centre that deals with non native invasive species, or safely and completely burn the material (details of permitted disposal sites: Natural Resources Wales)
Click on your county for council household waste recycling centre details (please check with your local facility if they accept cotoneaster waste before disposal)
Isle of Anglesey / Conwy / Denbighshire / Flintshire / Gwynedd / Wrexham

Silver studded blue butterfly © NWWT
Your support will help to protect our threatened species such as the hoary rock rose and the silver studded blue butterfly.
Identify the most dominant and invasive species of cotoneaster
Now considered in the top ten species having a negative impact on our protected sites in North Wales. Cotoneaster species are listed on the Schedule 9 to the Wildlife and Countryside Act 1981 England and Wales. Although still readily available to buy, it can be planted and contained in private gardens. However it is an offence to plant or otherwise cause these species to grow in the wild. GBNNSS
Cotoneaster ID link: ID_Cotoneaster_sp _(Cotoneaster) (nonnativespecies.org)
Entire leaved cotoneaster (C. integrifolius)
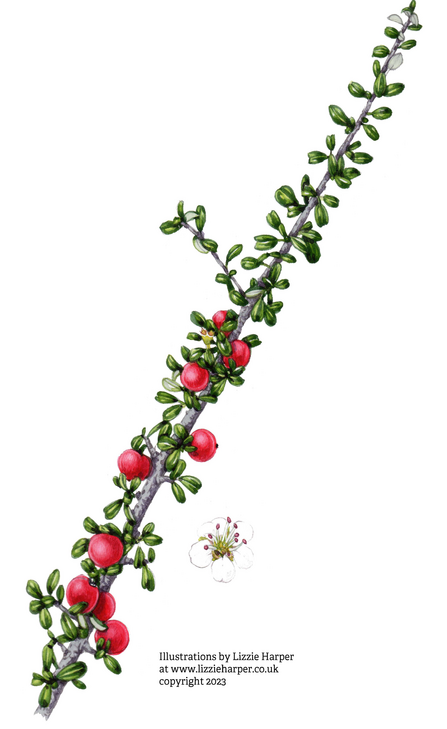

©Illustrations by Lizzie Harper at www.lizzieharper.co.uk copyright 2023 Entire leaved Cotoneaster (C. integrifolius)
- Evergreen low growing shrub
- Leaves: small elliptical, dark green and hairs underside
- Flowers: white, purple anthers
- Berries: late summer crimson colour, holds throughout winter
Himalayan cotoneaster (C. simonsii)

©Illustrations by Lizzie Harper at www.lizzieharper.co.uk copyright 2023 Himalayan cotoneaster (C. simonsii)
- Large hardy upright evergreen shrub
- Leaves: small none serrated, alternate along stem, glossy hairless upper and slight hairs on lower surface
- Flowers: pale pink, red patch centre of petal
- Berries: slightly larger, orange-red in clusters
Hollyberry cotoneaster (C. bullatus)

©Illustrations by Lizzie Harper at www.lizzieharper.co.uk copyright 2023 Hollyberry cotoneaster (C. bullatus)
- Much larger deciduous shrub up to 4 metres
- Leaves: matt green, oval and pointed, indented veins growing alternate on stem
- Flowers: pink, 5 petal, white anthers
- Berries: bright red, large slight square-shaped
Small leaved cotoneaster (C. microphyllus)
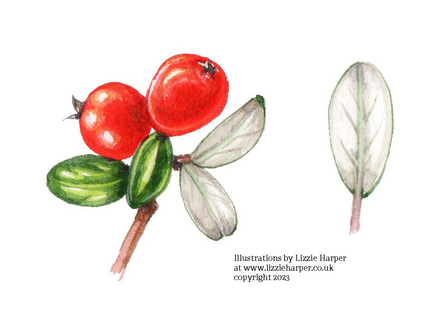
©Illustrations by Lizzie Harper at www.lizzieharper.co.uk copyright 2023 Small leaved cotoneaster (C. microphyllus)
- Evergreen low-lying shrub
- Leaves: glossy green top, grey/white underside, small (1cm length), elliptic
- Flowers: solitary white, 5 petals, dark violet anthers
- Berries: coral red and globular
Wall cotoneaster (C. horizontalis)

©Illustrations by Lizzie Harper at www.lizzieharper.co.uk copyright 2023 Wall cotoneaster (C. horizontalis)
- Deciduous low growing shrub: herringbone-shaped branches, stems woody dark brown, hard and knotty
- Leaves: small dark green upper, pointed and shiny on both sides, red in autumn
- Flowers: pink, 5 petal with white anthers
- Berries: orange-red
Here’s a handy guide to "Gardening without harmful invasive plants" including cotoneaster alternative shrubs (page 30) to keep your garden buzzing.
The GB Non-Native Species Secretariat has created useful "Tips for gardeners to Be Plant Wise" a campaign to help choose what to grow, how to stop the spread of invasive plants and composting with care after removal.
Questions or want to get involved? Contact us
Craig Wade, Limestone Grassland Restoration Project Officer

®Lottery Heritage Fund in partnership with Welsh Government
This project is funded by the Nature Networks Programme.
It is being delivered by the Heritage Fund, on behalf of the Welsh Government.





